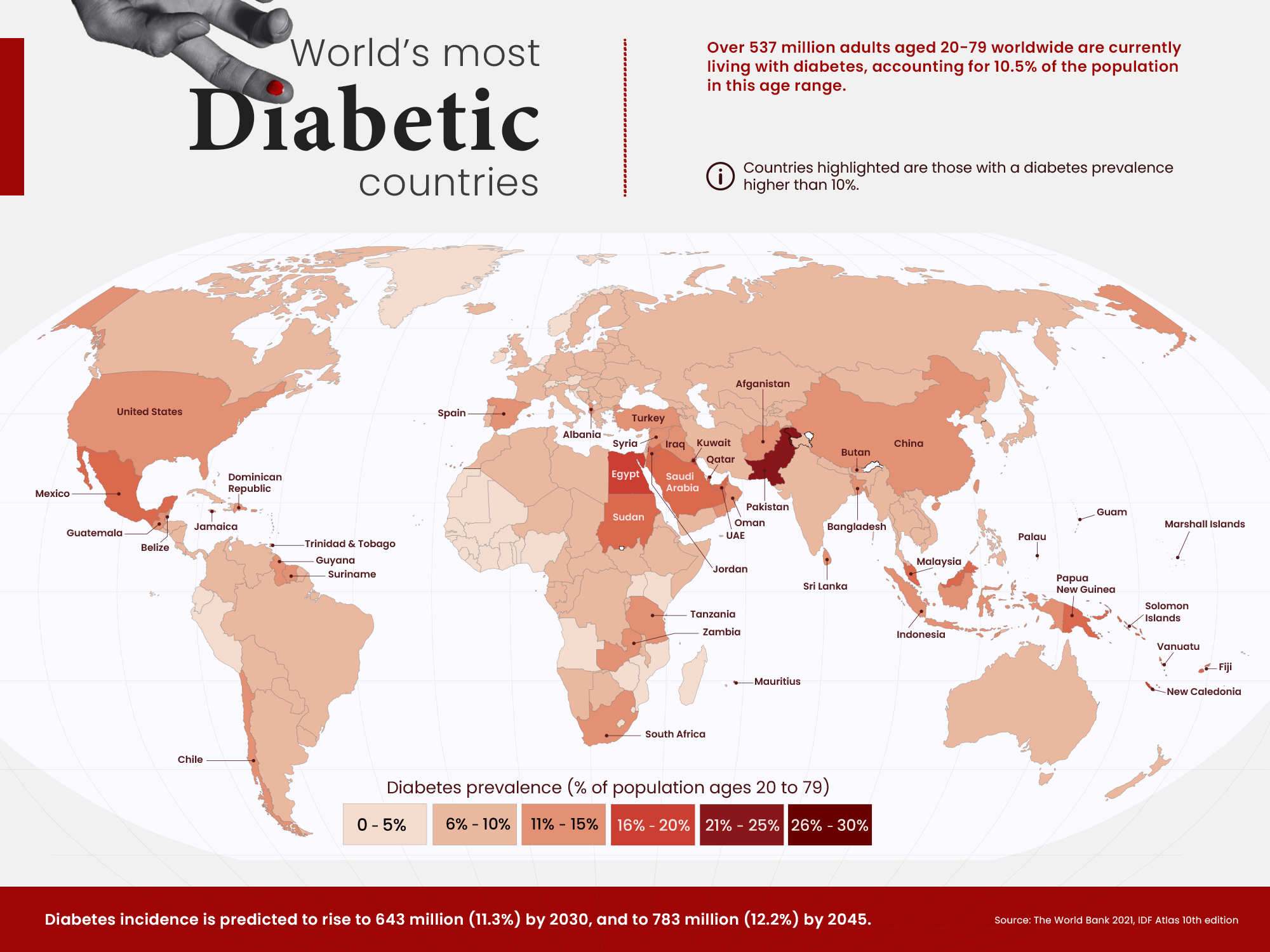
When it comes to identifying the most diabetic country, various factors need to be considered. These include prevalence rates, access to healthcare, lifestyle habits, and socioeconomic factors.
Pakistan has a noteworthy diabetes prevalence, with approximately 33 million people, or 31% of its population, suffering from the condition.
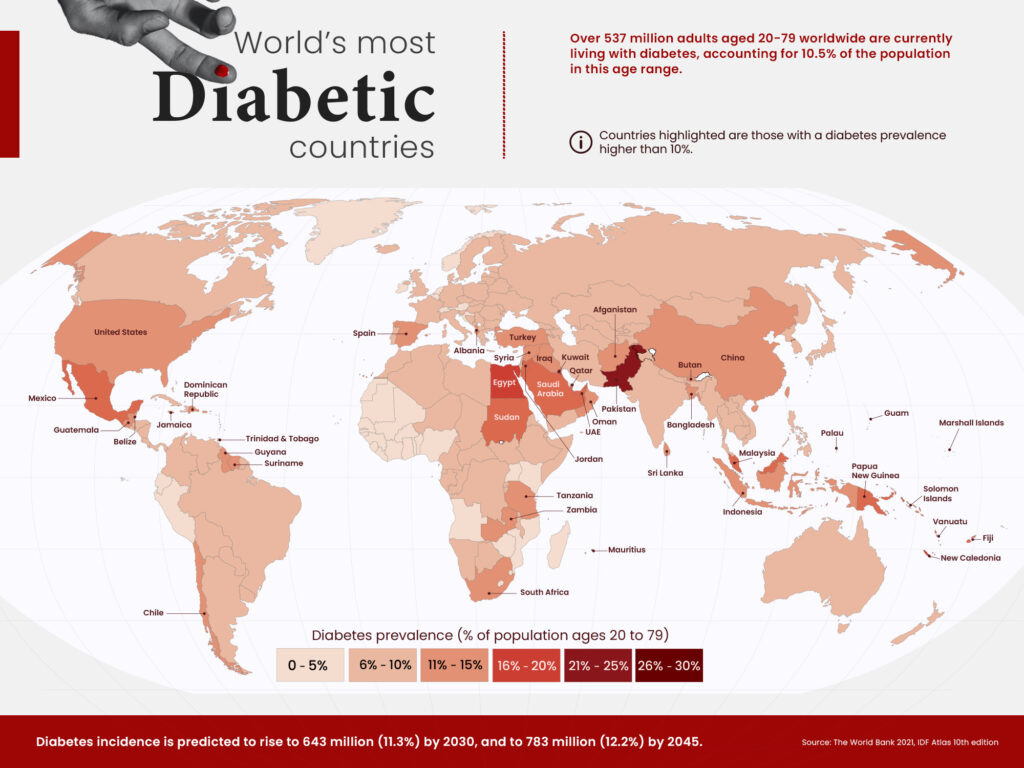
Pakistan has a high percentage of its population affected by diabetes, but in terms of the absolute number of individuals with the condition, China is the leader due to its larger population – approximately 140 million Adults have diabetes. Consequently, China’s percentage rate is comparatively lower.
India has a diabetes prevalence rate of 9.6%, which means that 77 million adults in the country suffer from the disease. This number is more than twice the number of people with diabetes in Pakistan.
In the Americas, Mexico has the highest prevalence of diabetes among adults, affecting 16.9% or 14.1 million individuals. The United States, on the other hand, has a lower percentage at 10.7%, but due to its larger population, an estimated 32.2 million American adults live with diabetes.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of awareness and education about diabetes. Many individuals in these countries are unaware of the risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of early detection and management of diabetes. This knowledge gap hinders prevention efforts and delays diagnosis.
The healthcare infrastructure in these countries may be inadequate to handle the growing burden of diabetes. Limited access to healthcare facilities, especially in rural areas, and a shortage of healthcare professionals can impede timely diagnosis and management of the condition.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or fails to use it effectively.
2. What are the different types of diabetes?
There are primarily two types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease, and type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with lifestyle factors.
3. What factors contribute to the high prevalence of diabetes?
The high prevalence of diabetes can be attributed to factors such as genetic predisposition, urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy dietary habits, and limited access to quality healthcare services.
4. How can diabetes be prevented and managed?
Prevention and management of diabetes involve adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and regular screenings. Medications and insulin therapy may also be prescribed by healthcare professionals.
5. What are the potential solutions to address diabetes?
Key strategies to combat diabetes include health education and awareness campaigns, strengthening healthcare systems, promoting healthy lifestyles, and addressing socioeconomic disparities.