The allure of the exotic and the pursuit of luxury have led to the rise of a unique trade that involves rare wood known as agarwood. It offers a glimpse into a captivating world where rare wood intertwines with big money.
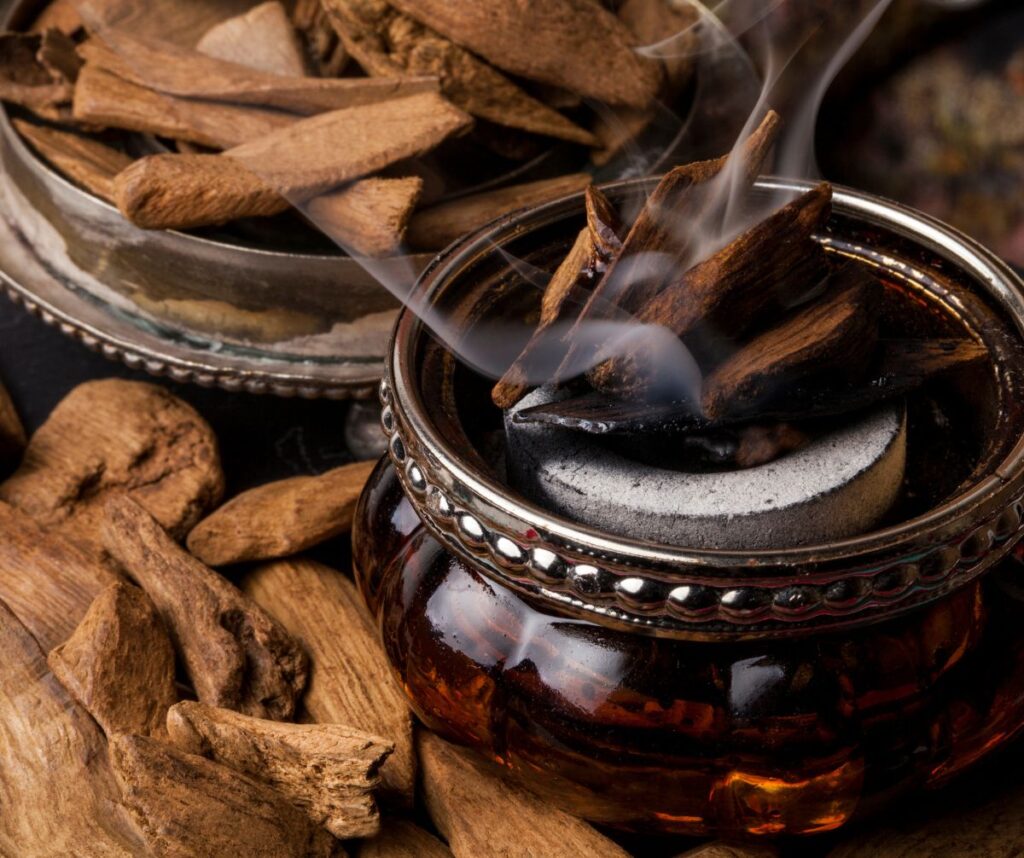

Agarwood is a fragrant dark resinous wood that forms within the Aquilaria trees when they become infected with a specific type of mould. This infection triggers a natural defence mechanism in the tree, forming resinous compounds in the heartwood.
Agarwood trees are native to various regions of Asia, including countries like India, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Malaysia. These trees grow in diverse ecosystems, ranging from rainforests to hilly terrains. Historically, agarwood was obtained from wild trees, but due to high demand, cultivation methods have been developed.
Natural agarwood is incredibly rare, making it highly sought after in the global market. The scarcity arises from the limited occurrence of infected trees and the lengthy maturation process required for agarwood to develop its characteristic aroma and resin.
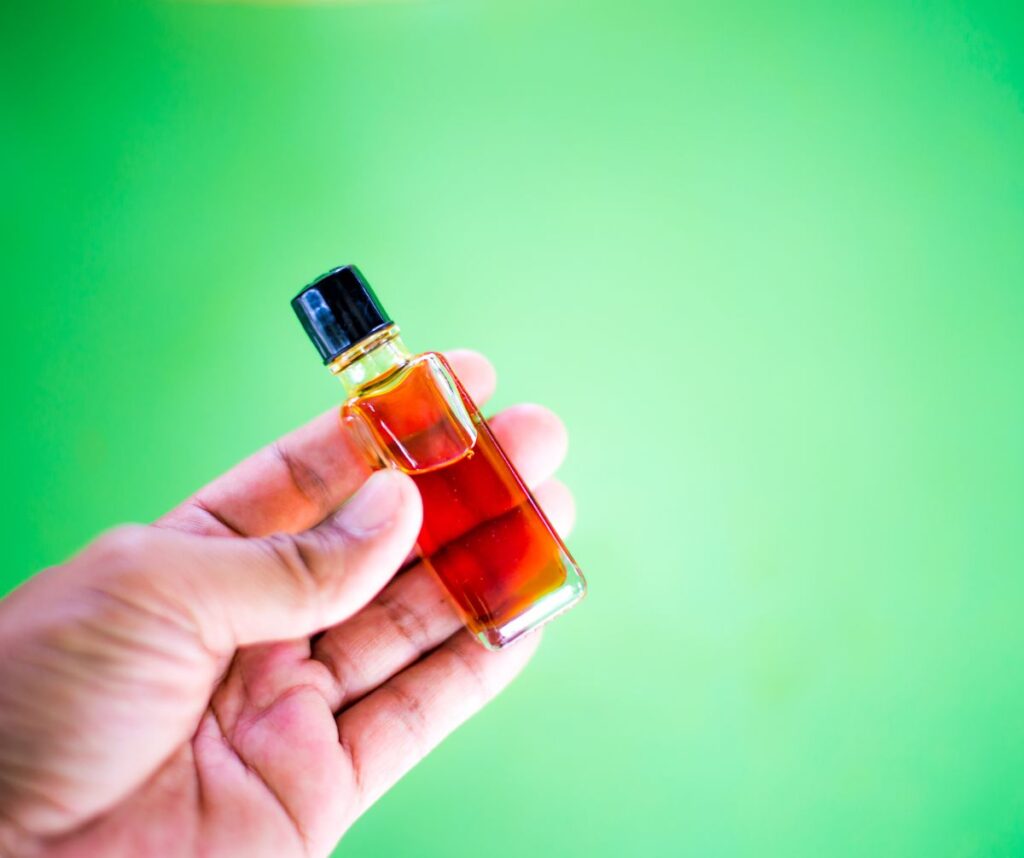

Agarwood is formed when Aquilaria trees become infected by a fungus called Phialophora parasitica. This natural infection is unpredictable and occurs in less than 10% of the Aquilaria population. Hence, the chances of finding naturally infected trees are exceptionally low.
Several species of Aquilaria trees are known to produce agarwood, including Aquilaria malaccensis, Aquilaria crassna, and Aquilaria sinensis. Each species has its unique characteristics, contributing to the diversity and value of agarwood in the market.
In the past, harvesters would search for agarwood trees in the wild and carefully extract the resinous heartwood. This process was labour-intensive and relied heavily on the knowledge and experience of the harvesters.
However, with the increasing demand, modern techniques have been developed to enhance production and meet market requirements.

Modern agarwood cultivation involves various techniques such as artificial infection, inoculation, and tissue culture. These methods allow for more controlled and predictable agarwood production, significantly reducing the pressure on wild resources.
Agarwood is in high demand, especially in the luxury fragrance industry. Its unique scent profile and long-lasting properties make it a prized ingredient in perfumes, incense, and other scented products. The rarity and labour-intensive process of obtaining agarwood contribute to its high prices.
Due to the increasing demand and unsustainable harvesting practices, the conservation of agarwood resources has become a pressing concern. Efforts are being made to promote sustainable practices and regulate trade through international agreements and regulations.
To protect wild agarwood resources, sustainable cultivation methods are being encouraged. This includes promoting responsible harvesting, implementing reforestation programs, and raising awareness about the importance of conservation.
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) plays a crucial role in regulating the trade of agarwood and its derivatives. Agarwood-producing countries work together to enforce regulations and prevent illegal trade.
The future of the agarwood trade relies on sustainable practices, responsible consumption, and effective regulation. As awareness grows regarding the conservation of endangered species and ecosystems, stakeholders are striving for a balance between demand and preservation. What do you think about this in-demand trade?

Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is agarwood illegal? No, agarwood itself is not illegal. However, the trade and harvest of agarwood are regulated to protect endangered species and ensure sustainable practices. It is essential to source agarwood from reputable and legal sources.
2. How is agarwood used in perfumes? Agarwood is distilled to extract oud oil, which is then used as an ingredient in perfumes. The unique aroma of oud oil adds depth and complexity to fragrance compositions, making it highly prized by perfumers.
3. Are there any health benefits associated with agarwood? Agarwood has been used in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits. It is believed to have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and calming properties. However, further scientific research is needed to validate these claims.
4. Can agarwood be cultivated? Yes, agarwood can be cultivated through various techniques such as artificial infection and tissue culture. Cultivated agarwood helps meet the demand while reducing pressure on wild resources.
5. How can I ensure the agarwood products I purchase are ethically sourced? To ensure ethical sourcing, look for reputable suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and support conservation efforts. It is also helpful to verify certifications and check if the supplier complies with CITES regulations.