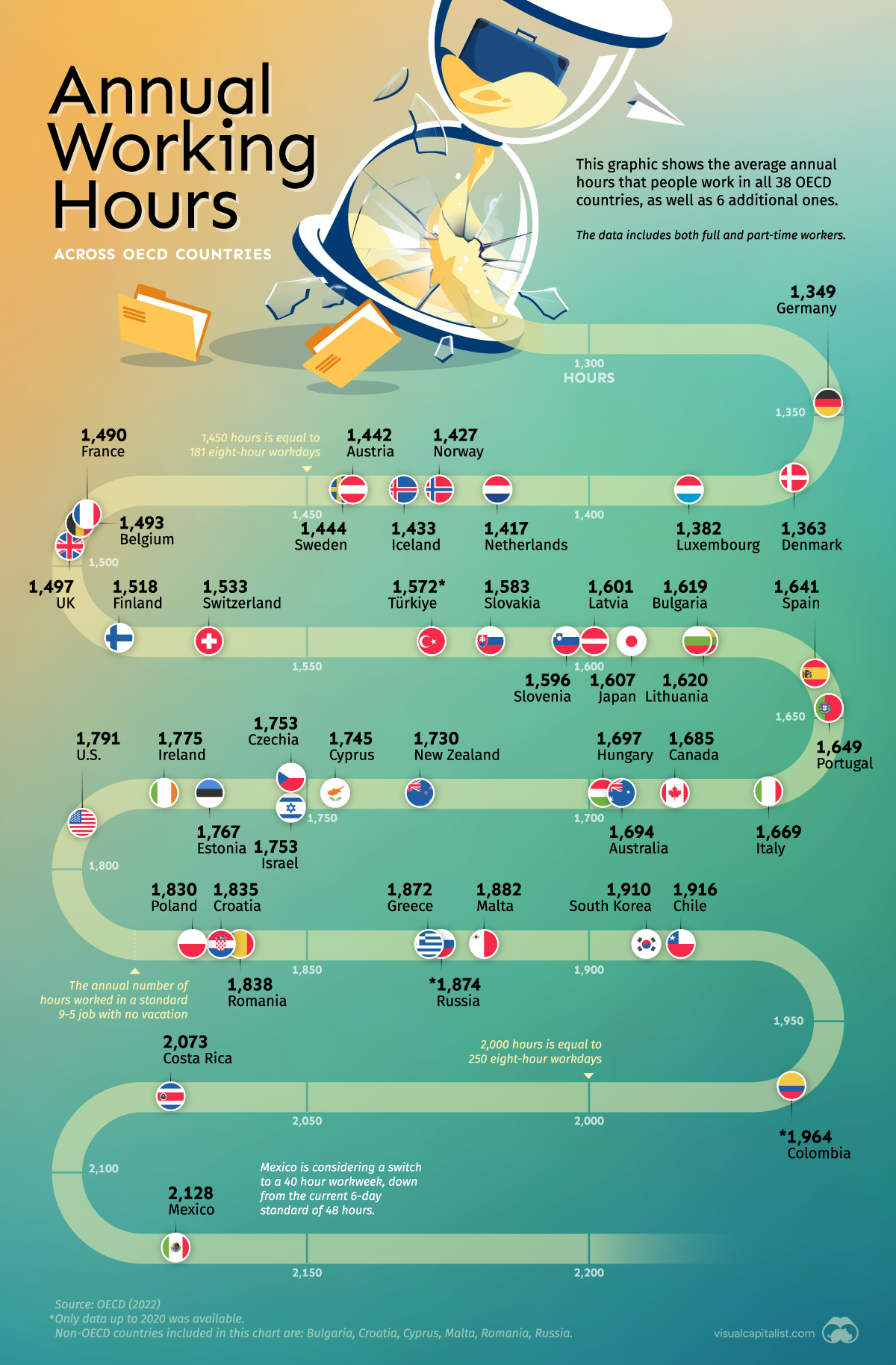
Annual working hours indicate the total hours worked in a year, including regular and overtime.

It is a crucial measure to evaluate a nation’s labour market, productivity, and work-life balance. Comparing OECD nations’ annual working hours offers information on economic factors.
Variation in Annual Working Hours
European Countries
European countries within the OECD generally exhibit lower annual working hours compared to countries in other regions.
This can be attributed to the emphasis on work-life balance and policies such as shorter working weeks, longer vacations, and generous parental leave.
North American Countries
North American countries, such as the United States and Canada, tend to have higher annual working hours compared to their European counterparts.
Factors contributing to this disparity include a stronger focus on economic productivity, a competitive work culture, and fewer labour regulations.
Asian Countries
Asian countries within the OECD, like South Korea, are known for their long working hours. This can be attributed to cultural factors, such as the importance placed on dedication and hard work, as well as economic factors driving productivity.
Australasian Countries
Australia and New Zealand strike a balance between European and North American countries regarding annual working hours. They prioritize work-life balance while maintaining competitive productivity levels.
Visualizing Annual Working Hours in OECD Countries
Here, we present a visual representation of the annual working hours in selected OECD countries:
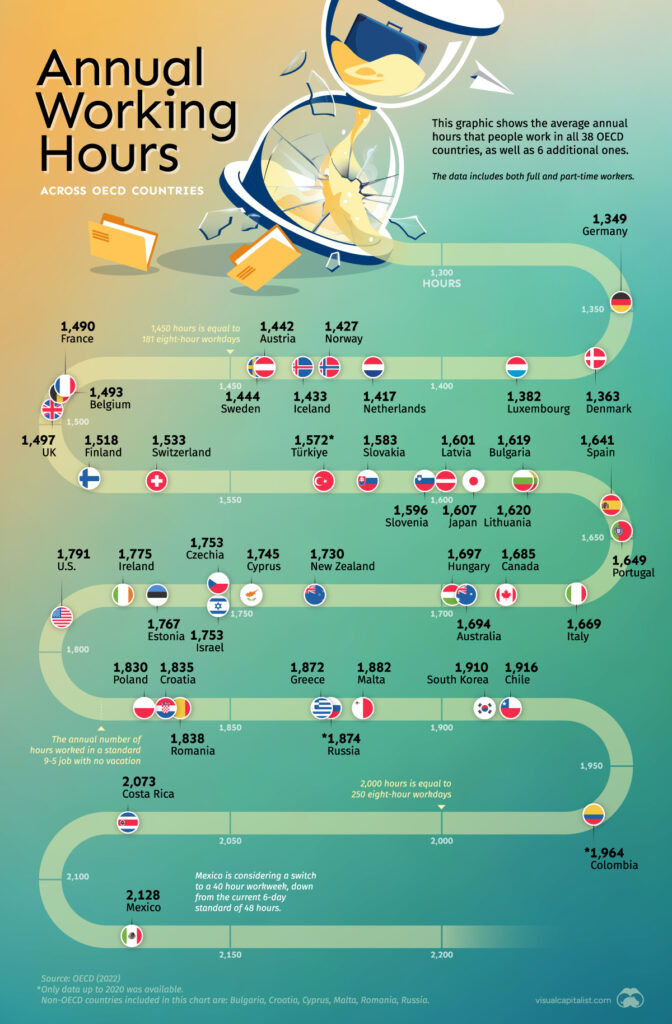
Understanding the variations in annual working hours across OECD countries is crucial in comprehending the diverse approaches to work, productivity, and work-life balance.
By visualizing these variations, we can gain valuable insights into the global labour market landscape.